Opening Hours - 9 AM to 5 PM
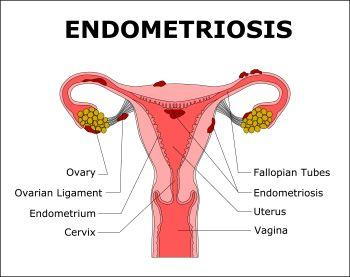
Endometriosis is a problem affecting a woman’s uterus—the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. Endometriosis is when the kind of tissue that normally lines the uterus grows somewhere else. It can grow on the ovaries, behind the uterus, on the bowels, or on the bladder. Rarely, it grows in other parts of the body.

Uterine fibroids are the most common noncancerous tumors in women of childbearing age. Fibroids are made of muscle cells and other tissues that grow in and around the wall of the uterus, or womb. The cause of fibroids is unknown. Risk factors include being African-American or being overweight. The symptoms of fibroids include
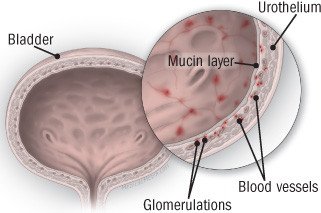
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder or surrounding pelvic region. People with IC usually have inflamed or irritated bladder walls that can cause scarring and stiffening of the bladder. IC can affect anyone; however, it is more common in women than men. Some people have some or none of the following symptoms:
Polycystic ovary syndrome happens when a woman’s ovaries or adrenal glands produce more male hormones than normal. One result is that cysts (fluid-filled sacs) develop on the ovaries. Women who are obese are more likely to have PCOS. Women with PCOS are at increased risk of developing diabetes and heart disease. Symptoms may include


STDs are infections that you can get from having sex with someone who has the infection. The causes of STDs are bacteria, parasites, and viruses. There are more than 20 types of STDs. Read more about specific STDs from these CDC fact sheets.
Most STDs affect both men and women, but in many cases the health problems they cause can be more severe for women. If a pregnant woman has an STD, it can cause serious health problems for the baby.
If you have an STD caused by bacteria or parasites, your health care provider can treat it with antibiotics or other medicines. If you have an STD caused by a virus, there is no cure, but antiviral medication can help control symptoms. Sometimes medicines can keep the disease under control. Correct usage of latex condoms greatly reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk of catching or spreading STDs.